Towards smart water monitoring: IoT-driven LSTM modelling for multi-step-ahead forecasting of river salinity dynamics
October 09, 2025
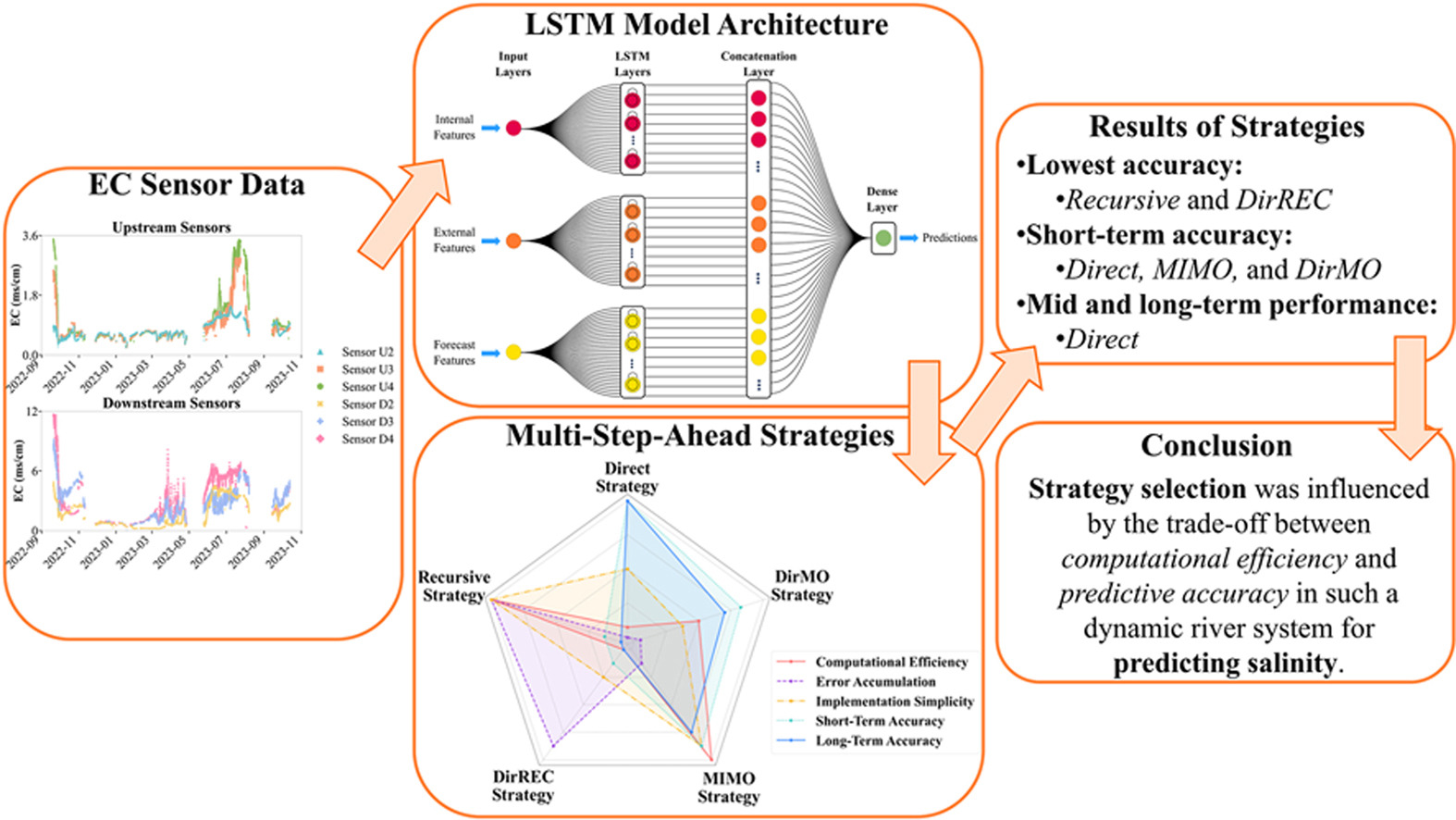
Effective water resource management increasingly depends on accurate forecasting of water quality parameters, particularly in dynamic river systems affected by saltwater intrusion. Electrical conductivity (EC), a key indicator of salinity, exhibits significant temporal and spatial variability, necessitating robust predictive models. This study aims to evaluate and compare the performance of five multi-step-ahead forecasting strategies (Direct, Recursive, DirREC, MIMO, and DirMO) using a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) modelling network applied to high-frequency IoT-based sensor data collected from a river system in a coastal region prone to seasonal salinity fluctuations. This study presents a comprehensive evaluation of multi-step-ahead forecasting strategies across short-term (4-h), mid-term (24-h), and long-term (48-h) horizons, supported by extensive hyperparameter tuning incorporating temporal and spatial features. The LSTM model's performance was also compared against state-of-the-art models, including Informer, DLinear, and PatchTST. Forecasting performance was assessed using Mean Squared Error (MSE), Percent Bias (PBIAS), and Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error (SMAPE). Results show that Direct, MIMO, and DirMO strategies consistently outperformed others across six sensor locations. Across all horizons, Direct achieved SMAPE values ranging from 1.3 % to 9.1 %, MIMO from 5.3 % to 25.2 %, and DirMO from 5.0 % to 22.6 %, with upstream locations showing slightly better performance due to more stable EC dynamics. In contrast, the Recursive and DirREC strategies exhibited error accumulation, particularly in long-term forecasts. These findings highlight the potential of forecasting techniques to reliably describe salinity dynamics but also underscore the importance of selecting appropriate forecasting strategies based on the required accuracy and computational efficiency.